
From Google Assistant to MQTT
Here I want to define a custom Google Assistant action, which will recognize a phrase with an argument, for example ok google, make me [a pizza], and send both the action (make) and the argument (a pizza) as a JSON object to an MQTT topic.
There’s a very easy way to recognize custom phrases in Google Assistant, by using the Google Assistant and IFTTT integration: there’s a Google Assistant trigger in IFTTT which guides you to do that, I won’t cover it here.
But, while IFTTT is a very useful service, with plenty of integrations available, to date, there’s no action that will publish to an MQTT.
Why use MQTT anyway? Well, I love MQTT because it’s very flexible, and it can be used in a lot of ways, to exchange messages and integrate things at home or across the Internet.
MQTT supports a lot of different clients, from libraries in you favorite programming language (search for paho), to command line (mosquitto) to implementations in higher level tools like one of my favorite: Node-Red.
The piece I’ll use to glue IFTTT to MQTT together is Beebotte, which has an excelent free plan for developers.
How will it work? in Beebotte we will create a channel and a resource. Data of any form (strings, numbers,…) can be published to a resource via a webhook (API). It is also possible to suscribe to the channel/resource via MQTT.
Create a channel in Beebotte:
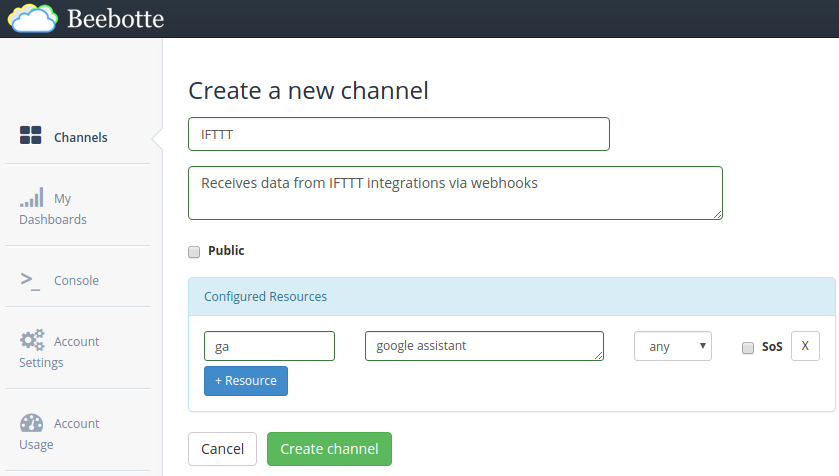
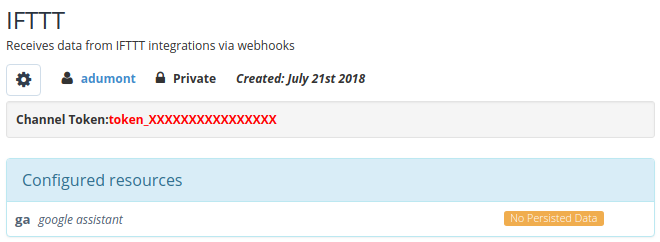
Now let’s enter in the channel, and take note of the token that has been assigned: token_XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX.
The key: How to subscribe to the Beebotte channel/resource via MQTT
- HOST: mqtt.beebotte.com
- PORT: 1883
- Username: token:token_XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
- Password: blank (don’t set password)
- TOPIC: channel/resource, here ifttt/ga
Read more here about MQTT - Beebotte Bridge and the Considerations)
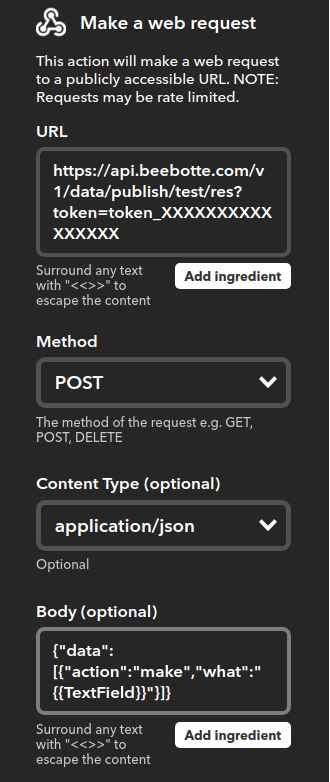
Now back in IFFFF, I’ll skip right to the point of creating the Action:
We’ll choose action type Webhooks, then “Make a web request” and use these fields:
- URL: https://api.beebotte.com/v1/data/publish/ifttt/ga?token=token_XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
- METHOD: POST
- Content Type: application/json
- BODY:
{"data":[{"action":"make","what":"{{TextField}}"}]}
What is important is the format of the body. It expects a data field, with an object. In the object, you can put whatever you want.
Here is an example of what is received on the MQTT end:
$ mosquitto_sub -h mqtt.beebotte.com -u token:token_XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX -t ifttt/ga -v
ifttt/ga {"data":[{"action":"make","what":"a pizza"}],"ispublic":true,"ts":1532185262619}
Now we can do whatever we want, for example from Node-Red. Each time I say “ok google, make me —” I’ll receive it as a message in the MQTT topic! Endless possibilities ahead!
